Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kato, Chiaki
Comprehensive Nuclear Materials, 2nd Edition, Vol.4, p.528 - 563, 2020/08
In spent fuel reprocessing plants, various nitric media are encountered throughout the PUREX process, used in the separation of fission products, uranium, and plutonium. The PUREX process is thus highly corrosive as it takes place at high temperatures under high concentrations of nitric acid solution containing oxidizing metal ions from spent fuel. In this review, the unique chemical properties of nitric acid are first described. Secondly, the process of oxidizing power generation in boiling nitric acid under heat transfer is described using the redox potential and a thermodynamic model of boiling nitric acid. Finally, the corrosion behavior and corrosion acceleration mechanism specific to the reprocessing environments are described from the perspective of solution chemistry.
Shirai, Osamu*; Yamana, Hajimu*; Arai, Yasuo
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 408-412, p.1267 - 1273, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:84.47(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Kato, Chiaki; Yano, Masaya*; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Sugimoto, Katsuhisa*
Corrosion Engineering, 52(1), p.53 - 67, 2003/01
The effects of heat-transfer on the corrosion of zirconium was examined in boiling nitric acid solutions with various concentrations. Corrosion mass losses and electrochemical polarization curves were measured on the heat-transfer and isothermal surfaces in the solutions. It was found that the corrosion rate of zirconium was higher on the heat-transfer surface than that on the isothermal surface. The rate increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature. The increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition on the surface and the removal of the decomposition product from solution by boiling bubbles. The redox potential of 12 mol/dm nitric acid on a boiling heat-transfer surface was very close to the breakdown potential of primary passivity of zirconium. This suggests the initiation of SCC on a boiling heat-transfer surface in a nuclear fuel reprocessing.
nitric acid on a boiling heat-transfer surface was very close to the breakdown potential of primary passivity of zirconium. This suggests the initiation of SCC on a boiling heat-transfer surface in a nuclear fuel reprocessing.
Kato, Chiaki; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Sugimoto, Katsuhisa*
Corrosion Engineering, 52(1), p.69 - 85, 2003/01
It is necessary to know the generation mechanism of high equilibrium potential in the solutions. Existing nitrogen oxides in nitric acid solutions were first analyzed by Raman spectroscopy and then existing amount of nitrogen oxides were examined by thermodynamic calculation using the SOLGASMIX software. The Raman spectroscopic analysis showed that the existing amount of un-dissociated HNO increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature. The thermodynamic calculation showed that the important nitrogen oxides in nitric acid solutions are HNO
increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature. The thermodynamic calculation showed that the important nitrogen oxides in nitric acid solutions are HNO , NO
, NO
 , HNO
, HNO , NO
, NO , and NO. The equilibrium potential of nitric acid solutions is, however, mainly decided by the HNO
, and NO. The equilibrium potential of nitric acid solutions is, however, mainly decided by the HNO /HNO
/HNO equilibrium. The thermodynamic calculation also suggested that the increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition of nitrous acid on the surface and the continuous removal of decomposition product from the solutions by boiling bubbles.
equilibrium. The thermodynamic calculation also suggested that the increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition of nitrous acid on the surface and the continuous removal of decomposition product from the solutions by boiling bubbles.
Kato, Chiaki; Yano, Masaya*; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Sugimoto, Katsuhisa*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 52(1), p.35 - 43, 2003/01
The effects of heat-transfer on the corrosion of zirconium was examined in boiling nitric acid solutions with various concentrations. Corrosion mass losses and electrochemical polarization curves were measured on the heat-transfer and isothermal surfaces in the solutions. It was found that the corrosion rate of zirconium was higher on the heat-transfer surface than that on the isothermal surface. The rate increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature. The increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition on the surface and the removal of the decomposition product from solution by boiling bubbles. The redox potential of 12 mol/dm3 nitric acid on a boiling heat-transfer surface was very close to the breakdown potential of primary passivity of zirconium. This suggests the initiation of SCC on a boiling heat-transfer surface in a nuclear fuel reprocessing.
Kato, Chiaki; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Sugimoto, Katsuhisa*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 52(1), p.44 - 52, 2003/01
In order to understand corrosion of metals in nitric acid solutions, it is necessary to know the generation mechanism of high equilibrium potential in the solutions, especially under boiling conditions. The Raman spectroscopic analysis showed that the existing amount of un-dissociated HNO increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature. The existing amount of NO
increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature. The existing amount of NO also increased by thermal decomposition. The thermodynamic calculation showed that the important nitrogen oxides in nitric acid solutions are HNO
also increased by thermal decomposition. The thermodynamic calculation showed that the important nitrogen oxides in nitric acid solutions are HNO , NO
, NO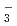 , HNO
, HNO , NO
, NO , and NO. The equilibrium potential of nitric acid solutions is, however, mainly decided by the HNO
, and NO. The equilibrium potential of nitric acid solutions is, however, mainly decided by the HNO /HNO
/HNO equilibrium. The thermodynamic calculation also suggested that the increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition of nitrous acid on the surface and the continuous removal of decomposition product from the solutions by boiling bubbles.
equilibrium. The thermodynamic calculation also suggested that the increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition of nitrous acid on the surface and the continuous removal of decomposition product from the solutions by boiling bubbles.
Mine, Tatsuya*; Mihara, Morihiro;
JNC TN8430 2000-009, 35 Pages, 2000/07
In the geological disposal system of TRU wastes, nitrogen generation by denitrifying bacteria could provide significant impact on the assessment of this system, because nitrate contained in process concentrated liquid waste might be electron acceptor for denitrifying bacteria. In this study, the activities and tolerance of denitrifying bacteria under disposal condition were investigated. pseudomonas denitrificans as denitrifying bacteria was used. The results showed that Pseudomonas denitrificans had activity under reducing condition, but under high pH condition (PH 9.5), the activity of Pseudomonas denitrificans was not detected. It is possible that the activity of Pseudomonas denitrificans would be low under disposal condition.
9.5), the activity of Pseudomonas denitrificans was not detected. It is possible that the activity of Pseudomonas denitrificans would be low under disposal condition.
J. A. BERRY*; M. BROWNSWORD*; D. J. ILETT*; Linklater, C. M.*; Mason, C.*; TWEED, C. J.*
JNC TJ8400 2000-060, 60 Pages, 2000/02
Batch sorption experiments have been carried out to investigate the sorption behaviour of plutonium onto basalt and sandstone from the appropriate rock-equilibrated waters under different redox eonditions. Redox Potentials in solution were controlled by the addition of two reducing agents and one oxidising agent. Thermodynamic chemical modelling was undertaken to interpret the results. The sorption models were based on iron oxide. They adequately reproduced the data for sorption of plutonium onto sandstone, but tended to underpredict sorption onto basalt.
Sato, Haruo
JNC TN8400 99-060, 12 Pages, 1999/10
Apparent diffusion coefficients(Da) of Cs(Cs ), Ni(Ni
), Ni(Ni ) and Se(SeO
) and Se(SeO
 ) in a Na-bentonite (Kunigel-V1) were measured for a dry density of 1.8 Mg
) in a Na-bentonite (Kunigel-V1) were measured for a dry density of 1.8 Mg m
m with silica sand of 30 wt% at room temperature by in-diffusion method to evaluate the effect of the mixture of silica sand on Da in bentonite. The experiments for Cs and Ni were carried out under aerobic condition, but those for Se which is redox sensitive were carried out in an Ar glove-box (O
with silica sand of 30 wt% at room temperature by in-diffusion method to evaluate the effect of the mixture of silica sand on Da in bentonite. The experiments for Cs and Ni were carried out under aerobic condition, but those for Se which is redox sensitive were carried out in an Ar glove-box (O concentration
concentration  0.1 ppm). Consequently, no significant effect of silica sand mixture to the bentonite on Da values of Cs and Se was found, and the obtained Da values were approximately the same as those in the system without silica sand reported so far. On the other hand, Da values of Ni in bentonite with silica sand were 2 orders of magnitude lower than those in bentonite without silica sand obtained to date. The Da values of Ni reported so far were obtained using stable isotopic tracer and a tracer solution with fairly high Ni concentration compared with concentration used in this study was introduced. Additionally, it is known that distribution coefficient (Kd) of Ni on Na-montmorillonite which is the major constituent clay mineral of Kunigel-V1 decreases with increasing Ni concentration. Based on this, the abrupt decrease in Da values of Ni for bentonite with silica sand is considered to be due to the difference of sorption caused by the difference of Ni concentration in the porewater of bentonite.
0.1 ppm). Consequently, no significant effect of silica sand mixture to the bentonite on Da values of Cs and Se was found, and the obtained Da values were approximately the same as those in the system without silica sand reported so far. On the other hand, Da values of Ni in bentonite with silica sand were 2 orders of magnitude lower than those in bentonite without silica sand obtained to date. The Da values of Ni reported so far were obtained using stable isotopic tracer and a tracer solution with fairly high Ni concentration compared with concentration used in this study was introduced. Additionally, it is known that distribution coefficient (Kd) of Ni on Na-montmorillonite which is the major constituent clay mineral of Kunigel-V1 decreases with increasing Ni concentration. Based on this, the abrupt decrease in Da values of Ni for bentonite with silica sand is considered to be due to the difference of sorption caused by the difference of Ni concentration in the porewater of bentonite.
Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Yui, Mikazu; Savage, D.*; Bille, B.*
JNC TN8400 99-025, 32 Pages, 1999/06
Groundwater data used for modelling site or repository evolution need to be assessed for their quality and whether they are "fit for purpose", prior to utilization. This report discuss factors and issues which impinge upon the quality of such data. It is recommended that geochemical modelleres : (1)are aware of how groundwater samples were collected, whether during drilling, during hydraulic testing, or thereafter, by in-situ measurement, pumped from boreholes, or by pressurised sampler ; (2)are aware of what procedures (if any) were used to "correct" samples for drill fluid contamination and what errors were associated with those methods ; (3)are aware of whether samples were subject to de-pressurisation during sampling, and whether geochemical modelling techniques were applied to correct the compositions of samples for that process ; (4)request different measures of redox activity (e.g., electrode measurements of Eh, concentrations of different redox-sensitive aqueous species) to be applied to key groundwater samples to investigate the extent of redox equilibrium ; (5)are aware of how groundwater samples were filtered and preserved for off-site analysis ; (6)ensure that adequate methods of groundwater filtration ( 0.1
0.1 m) and chemical analysis are applied to ensure accurate and reproducible analyses for dissolved aluminum at low levels of concentration (generally less than 0.2 mg/L) ; (7)are aware of elemental errors and detection limits in chemical analysis of groundwater samples and assess the quality of groundwater analyses via ion exchange balances and via a comparison of measured and calculated values for total dissolved solids contents. (8)ensure that detailed mineralogical analysis is carried out on rock samples from locations where key groundwater samples have been extracted.
m) and chemical analysis are applied to ensure accurate and reproducible analyses for dissolved aluminum at low levels of concentration (generally less than 0.2 mg/L) ; (7)are aware of elemental errors and detection limits in chemical analysis of groundwater samples and assess the quality of groundwater analyses via ion exchange balances and via a comparison of measured and calculated values for total dissolved solids contents. (8)ensure that detailed mineralogical analysis is carried out on rock samples from locations where key groundwater samples have been extracted.
Imai, Hisashi*; Amemiya, Kiyoshi*; Nishida, Kaoru*; Lin, Weiren*; *
PNC TJ1449 97-002, 261 Pages, 1997/03
no abstracts in English
Imai, Hisashi*; Amemiya, Kiyoshi*; Nishida, Kaoru*; Lin, Weiren*; *; Senna, Shigeki*
PNC TJ1449 96-005, 76 Pages, 1996/03
None
Amemiya, Kiyoshi*; Imai, Hisashi*; Chijimatsu, Masakazu*; Nishida, Kaoru*; Lin, Weiren*; Senna, Shigeki*
PNC TJ1449 95-006, 69 Pages, 1995/03
no abstracts in English
Maeda, Toshikatsu; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Bamba, Tsunetaka; *
JAERI-Research 95-019, 18 Pages, 1995/03
no abstracts in English
Ishikawajima-Harima Heavy Industries*
PNC TJ1150 94-001, 19 Pages, 1994/03
None
Chikasui Gijutsu, 36(12), p.4 - 19, 1994/00
no abstracts in English
Aoyama, S.*; Ishii, T.*; Horita, M.*; Adachi, T.*; Horie, Y.*; Hokari, T.*
PNC TJ1060 92-001, 240 Pages, 1992/03
None